MAIN TYPES OF COMPUTERS

It isn’t easy to imagine modern life without a computer so here we will list 7 types of computers that will help you choose the right one for your business. We use computers to complete tasks, have fun, and learn new things. We occasionally forget that our smartphone is essentially a miniature desktop computer.
Most people define a computer as one that accepts mouse or keyboard input, process it, and displays the result on a screen. Computer hardware and software have advanced at breakneck speed in recent years; the heavy desk-crushing machines of the early 1980s are incomparable to today’s light touchscreen tablets.
The various types of computers are described using a variety of terms.Most of these terms refer to the computer’s size , purpose , or capabilities. Let us now move on from the most obvious.
DESKTOP
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop. Desktop is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a case that houses the power supply, motherboard (a printed circuit board with a microprocessor as the central processing unit, memory, bus, certain peripherals and other electronic components), disk storage (usually one or more hard disk drives , solid -state drives); optical disc drives, and in early models floppy disk drives); a keyboard and mouse for input ;and a monitor, speakers, and often , a printer for output . The case may be oriented horizontally or vertically and placed either underneath besides, or on top of a desk.
PERSONAL COMPUTER
A personal computer is designed for general use by a single personal (PC). Even through an iMac is undeniably a PCs were initially known as microcomputers because they were complete computers built on a smaller scale than the massive systems used by most businesses.
In 1981, IBM released its personal computer, which ran Microsoft’s now- iconic MS Dos operating system Apple introduced the Lisa, one of the first personal computers with a graphic user interface, in 1983. Alternatively, “icon ” could be seen on the screen. Previously, computer screens were relatively simple.
CPU (Central Processing unit) and RAM (Random access memory) have evolved rapidly over time, allowing computers to run more efficiently. Compaq introduced a 32 – bit CPU for its 386 computers in 1986. Intel cemented its place in computer history with the release of the first Pentium processor in 1993. Touchscreens, multiple built -in connectivity option and constantly evolving operating systems are all features of today’s personal computers. The dimensions and shapes of the machines are also dissimilar.
SUPERCOMPUTER
A Supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compares to a general-purpose computer. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computer science and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in various fields including quantum mechanics, weather forecasting, climate research, oil and tags exploration, molecular modeling and physical simulation. They have been essential in the field of cryptanalysis.
The Performance of supercomputer is commonly measured in floating -point operations per second instead of million instructions per second. Since 2022, exascale supercomputers have exited which can perform over 10 FLOPS. For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigga FLOPS to tens of tera Flops. Since November 2017, all of the world’s fasters 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating system. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan,Japan,and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.
MINI COMPUTER
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of general-purpose computer mostly developed from the mid-1960, built significantly smaller and sold at a much lower price than mainframe computers. Minicomputers are small relative to earlier and bigger machines.
The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching, as distinct from calculation and record keeping.Many were sold indirectly to orignal equipment manufactures for final end -use application . During the two decade lifetime of the minicomputer class, almost 100 minicomputer vendor companies formed . only a half -dozen remained by the mid- 1980.
MAINFRAME COMPUTER
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe,maxicomputer , or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organization for critical application like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large -scale computer system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers.
The term mainframe was derived from the large cabinet, called a main frame, that housed the central processing unit and main memory of early computers. Later, the term mainframe was used to distinguish high-end commercial computers from less powerful machines.
WORKSTATION COMPUTER
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific application. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term workstation has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphic, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphic revolution of the late1990s.
Workstations formerly offered higher performance specification than mainstream personal computers, especially in teams of processing, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the visualization and manipulation of different types of complex data such as 3D mechanical design, engineering simulations like computational fluid dynamics, animation, video editing, image editing, medica imaging, image rendering, computational science, generating mathematical plots, and software development. Typically, the form factor is that of a desktop computer, which consists of a high-resolution display, a keyboard ,and a mouse at a minimum, but also offers multiple displays, graphic tablets, and 3D mice for manipulating objects and navigating scenes. Workstations were the first segment of the computer market to present advanced accessories, and collaboration tools like videoconferencing.
ANALOG COMPUTER
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine that uses physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities behaving according to the mathematical principles in question to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discreate values of both time and amplitude.
Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while navel gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/ analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective s\functions. The common Property of all of them is that they don’t use algorithms to determine the fashion to how the computer works. They rather use a structure analogous to the system to be solved which is also eponymous to the term analog computer, because they represent a model.
DIGITAL COMPUTER
The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. The word digital implies that the information in the computer is represented by variable that take a limited number of discrete states. The decimal digits 0,1,2, ……,9, for example, provide 10 discrete values. The first electronic digital computers, developed in the late 1940s, were used primarily for numerical computations. In this case the discrete elements are the digits. From the application the term digital computer has emerged. In practice, digital computers functions more reliably if only two statuses are used Because of the physical restriction of components, and because human logic tends to be binary, digital components that are constrained to take discrete values are further constrained to take only values and are said to be binary.
Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two digits:0 and 1 binary digit is called a mi. information is represented in digital computer in group of bits. By using various coding techniques, groups of bits can be made to represent not only binary numbers but also other discrete symbols, such as decimal digits or letters of the alphabet. By judicious use of binary arrangements and by using various coding techniques, the group of bits are used to develop complete sets of instructions for performing various types of computations.
In contrast to the common decimal numbers that employ the base 10 system, binary number use a base 2 system with two digits:0 and 1. The decimal equivalent of a binary number can be found by expanding in into a power series with a base of 2. For example, the binary number 1001011 represents a quantity that can we converted to a decimal number by multiplying each bit by the base 2 raised to an integer power as follow:
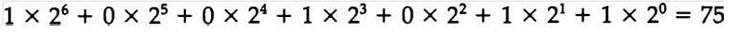
HYBRID COMPUTER
Hybrid computer are computers that exhibit features of analog computers and digital computers. The digital components normally serve as the controller and provides logical and numerical operations, while the analog components often serve as a solver of differential equations and other mathematically complex problems.
Hybrid computer can be used to obtain a very good but relatively imprecise “seed ‘value, using an analog computer front-end, which is then fed into a digital computer iterative process to achieve the final desired degree of pericon. With a three or four digit, highly accurate numerical seed, the total digital computation time to reach the desired precision is dramatically reduced, since many fewer iterations are required. One of the main technical problems to be overcome in hybrid computers is minimizing digital-computer noise in analog computing elements and grounding system.





Leave a Reply